Karenia mikimotoi (Miyake & Kominami ex Oda) Gert Hansen & Moestrup 2000
Current name:
Karenia mikimotoi (Miyake & Kominami ex Oda) Gert Hansen & Moestrup
Ireland.Caroline Cusack (robin.raine@nuigalway.ie)
Publication Details
Karenia mikimotoi (Miyake & Kominami ex Oda) Gert Hansen & Moestrup 2000: 308
Published in: Daugbjerg, N., Hansen, G., Larsen, J. & Moestrup, Ø. (2000). Phylogeny of some of the major genera of dinoflagellates based on ultrastructure and partial LSU rDNA sequence data, including the erection of three new genera of unarmoured dinoflagellates. Phycologia 39: 302-317.
Type Species
The type species (holotype) of the genus Karenia is Karenia brevis (C.C.Davis) Gert Hansen & Moestrup.
Status of Name
This name is of an entity that is currently accepted taxonomically.
Basionym
Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda
Type Information
Type locality: NW Pacific Ocean: Gokasho Bay, Japan; (Faust & Gulledge 2002: 40) Holotype: (Faust & Gulledge 2002: 40)
General Environment
This is a marine species.
Description
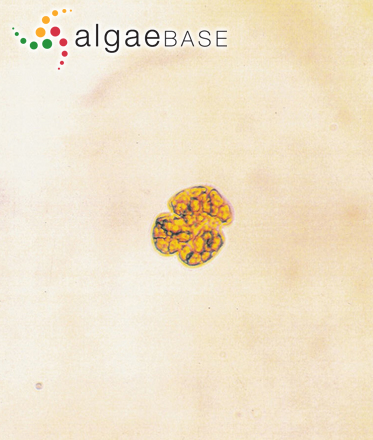
A photosynthetic species with several oval to round yellow-brown chloroplasts, each with a pyrenoid. The large ellipsoidal nucleus is located in the left hypothecal lobe. No thecal plates are present. Cells are small, broadly oval to almost round and compressed dorso-ventrally. Cells are slightly longer than wide with a characteristic long and straight apical groove to the right of the sulcal axis. The apical groove extends from the ventral side to the dorsal side of the epitheca creating a slight indentation at the apex of the cell. Cells range in size from 18-40 µm in length to 14-35 µm in width .The epitheca is broadly rounded and smaller than the hypotheca. The hypotheca is notched by the widening sulcus at the antapex resulting in a lobed posterior. The wide and deeply excavated cingulum is pre-median, and is displaced in a descending spiral about 2 times its width. The sulcus slightly invades the epitheca extending from above the cingulum to the antapex (adapted from http://www.nmnh.si.edu/botany/projects/dinoflag/Taxa/Gmikimotoi.htm).
Habitat
A planktonic species first described from western Japan. This species is a recurring bloom former in coastal waters of Japan and Korea; red tides commonly occur in warmer months and are associated with massive fish and shellfish kills. Reported to be eurythermal and euryhaline, populations of G. mikimotoi could presumably over-winter as motile cells, which could then serve as seed populations for a summer red tide. Moreover, studies conducted in Omura Bay, Japan, revealed that this species can tolerate anoxic or near anoxic conditions utilizing sulfide from the sediment.
Key Characteristics
Cells have a distinct swimming pattern: turning over through water, like a falling leaf.
Created: 26 April 2002 by M.D. Guiry.
Last updated: 28 May 2024
Verification of Data
Users are responsible for verifying the accuracy of information before use, as noted on the website Content page.
Usage note
First described from Japan in 1935, this species was found in the Atlantic in 1957 on the east coast of the USA, and, in 1966, it bloomed off the coast of Norway. It appears to have been spread in ballast water and is now a major cause of algal blooms throughout the world. A major bloom took place in the English Channel in 2003. It was first found in Irish waters in 1976, and it bloomed in successive years from 1978 and 1982, and again from 1990 to 1995. In 2005, a enormous bloom off the west coast of Ireland covered many hundreds of square kilometers of coastal waters and caused major 'kills' of marine organisms including fish, shellfish, brittle stars, and farmed salmon and cod. The "Irish Times" of August 6, 2005 quoted Kevin Flannery, Sea Fisheries Officer with the Department of the Marine: "We are now talking about huge marine dead zones." Harmful species (Lassus et al. 2017). - (11 May 2006) - G.M. Guiry
Linking to this page: https://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?species_id=44334
Citing AlgaeBase
Cite this record as:
M.D. Guiry in Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. 28 May 2024. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. https://www.algaebase.org; searched on 28 March 2025
 Request PDF
Request PDF














